What is the Market Summary Report?
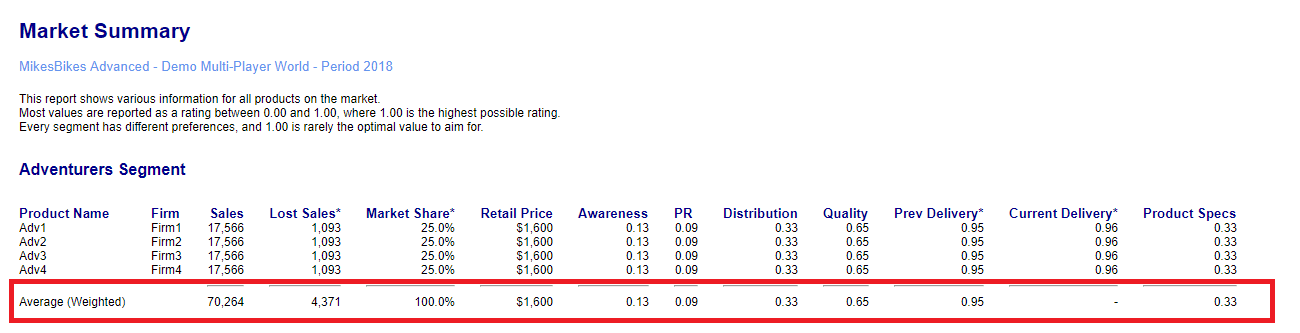
The Market Summary Report gives a side-by-side comparison of all the products currently being sold in the market. It compares every product on the key features that help consumers decide which product to buy.
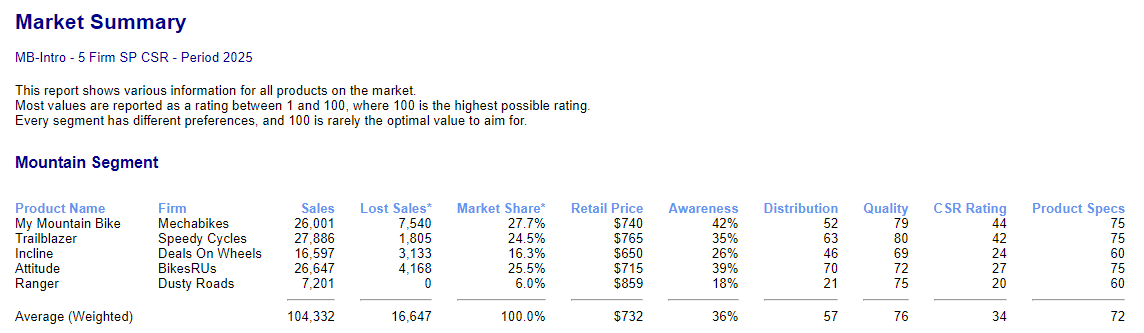
Some of these features are more important than others to each Market Segment. For instance, the Road segment is highly sensitive to Quality and Product Specifications, but does not care as much about Price. But the Kids segment is highly sensitive to Price and Awareness but does not care much about Quality. So you need a different strategy to succeed in each market.
You should read the Market Research report to see which features are most important to each Market Segment.
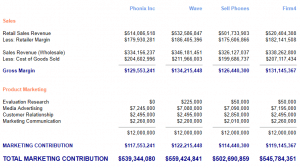
Sales, Lost Sales, and Market Share
Sales is simply how many units that each product sold last year.
Lost Sales tells you how many more units each product would have sold if that Firm had manufactured enough to satisfy demand. If Lost Sales is zero for a given product, then the Firm produced enough to meet all the demand for that product this year.
Example: If there are 20,000 units of demand for a product, and 18,000 units available for sale,
then Lost Sales = 2000 units
Market Share shows the share that each product has of total market demand (ie. including Lost Sales).
Retail Price
Retail Price is the recommended retail price that each firm sets for their product(s). So if your Retail Price is $700 and your average retailer margin is 35%, then the wholesale price that you receive from your distributors for each bike is $455. But the Retail Price is what consumers actually pay, so Retail Price is what they compare when deciding which product to purchase.
Awareness
Awareness % is a measure of how many consumers in each market segment remember and know something about your product due to your brand promotion and product advertising.
Awareness of 50% means that 50% of the consumers in that segment are aware of your product. When trying to raise the awareness level of your product(s), you need to pay attention to making sure that you are targeting your budgets to the media types that each market segment watches the most.
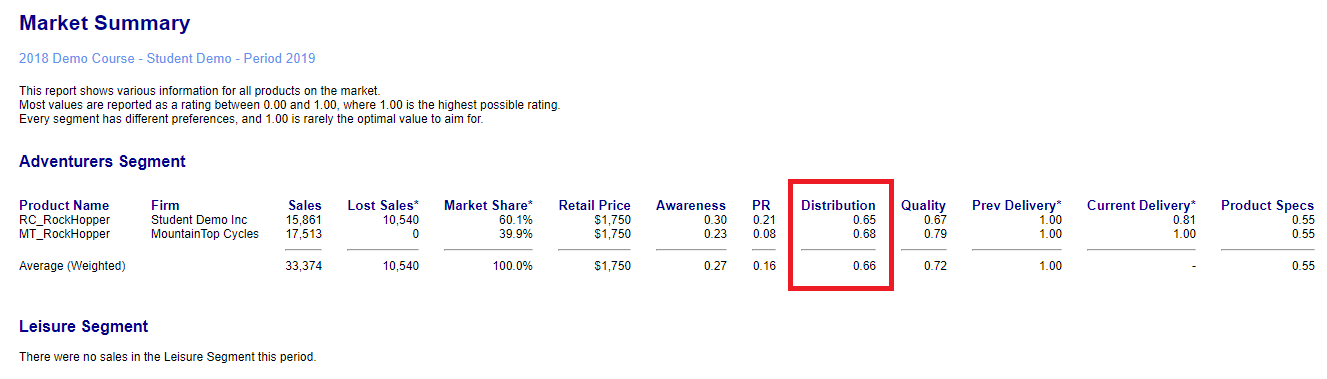
Distribution
The Distribution Rating (1 to 100) is a measure of what proportion of the consumers in each market segment can easily find your products at a local store without having to travel too far.
In general, as your sales volumes and retail margins increase then more stores will be willing to stock your products and your Distribution Rating will increase. Once you have established significant sales volume in a market you may be able to reduce your retail margins slightly without losing too many stores.
Quality
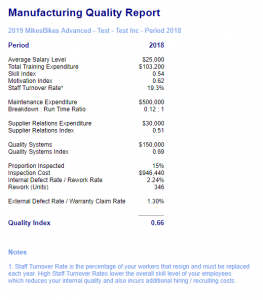
Quality refers to the level of customer satisfaction in your product based on finish, workmanship, and the rate of product defects. This is measured using a Quality Rating out of 100 which applies to all your company’s products.
See the Quality screen under the Operations menu.
Product Specs
The Product Spec Rating is a measure from 1 to 100 of how close your product is to a perfect or ideal bike for that Market segment. From Year 4 onwards you will be able to conduct Product Development to improve the specifications of your bikes and Cost Reduction to reduce the Prime Cost of your bikes.
CSR Rating (Corporate Social Responsibility)
Corporate Social Responsibility (CSR) is a concept which sees companies being responsible not only for profit maximization, but also to do what’s best for people, the planet and society at large. Your CSR rating is a measure of how well your company integrates social and environmental concerns with its business operations.
Your CSR Rating is affected by your Social Responsibility decisions (under Brand Promotion from Year 2) and Sustainable Manufacturing decisions (under Operations from Year 3).
Note: If you do not see the CSR Rating, then your course is not using the Brand Promotion and Sustainable Manufacturing decisions.
Comparing Product Ratings
Don’t get too obsessed with trying to achieve a specific Awareness, Distribution, Quality, or Product Spec Rating. The important thing is to use the Market Summary report as a benchmarking tool to see how your products compare with your competitors.
If your competitors have a much cheaper product, or much higher product specs or quality than you then you may need to invest more in those areas to compete. But if you already have significantly higher Quality or Awareness than your competitors then at some point diminishing returns will kick in and you may be better investing more into other areas of your business.
Also remember to read the Market Research report to see which features are most important to each Market Segment so you aren’t wasting time and money on something which won’t really make much difference to a particular market.